Tech Opportunities That Influence Your Organic Rankings
You have your content generation strategy ready. You have lined up the influencers. You have learned and invested in Facebook ads. Regardless of all the ways, you try to get traffic to your website, if your underlying website is not up to par, you are not going to get the holy grail of all – organic traffic. For modern search engines to index and process your website and send traffic your way, you need to optimize your website on a technical level for those search engines. This is called Technical SEO and just like On-Page or Off-Page SEO your website will live or die by it. Here is a master checklist of technical SEO opportunities:
Register Site with Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools
This should be the first step as it will let Google or Bing know to crawl your website and index it. This should be the first step to perform on a new site.
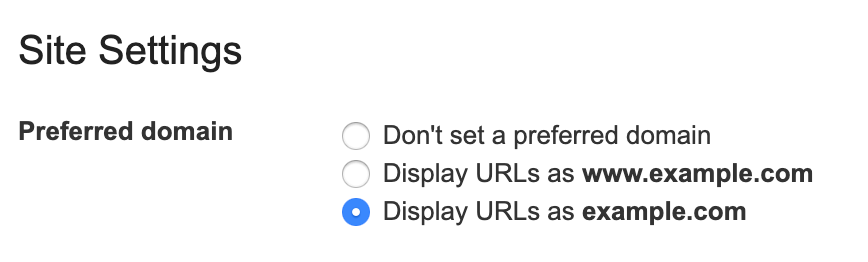
Set a Preferred Domain
A website can be reached at either https://www.site-name.com or https://site-name.com. Search engines treat these as two different websites. You can run into indexing issues, loss of page rank and duplicate content problems. This setting can be set in your CMS.
Best Practices for robots.txt
This lets the search engine know which pages on the site can be crawled and added to their index. This where single out URLs on your site that you do not want crawled and indexed. This is a simple thing to set up but also very easy to mess up. Any false blocks in the file will prevent the search engine crawler from indexing your site.
Pay Attention to URL Structure
It is recommended to keep the URLs short and descriptive. Avoid using unnecessary characters or words in them. Words should be separated with a hyphen and should most likely be the target keywords of the page. Avoid keyword-stuffing in the URL. If you are using WordPress as your CMS then it takes care of this for you. For example, https://site-name.com/page-about-technical-seo is a good name to select for your URL.
Navigation and Website Structure
As long as your site structure is logical and easy to understand it will be easier for the search engine to crawl and classify. Don’t put all the pages under one category page. Separate them logically as a user might. Google takes into account the entire structure of a website when indexing a page.
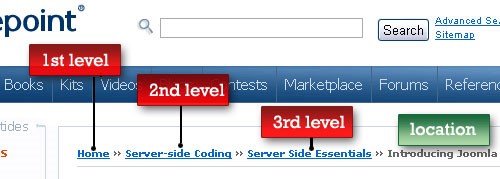
Add Breadcrumb Menus
These are mentioned and recommended by Google. They should have a proper schema as the search engine will deduce the site structure from the breadcrumbs. It will help the search engine and the users navigate the website without having to press the back button.
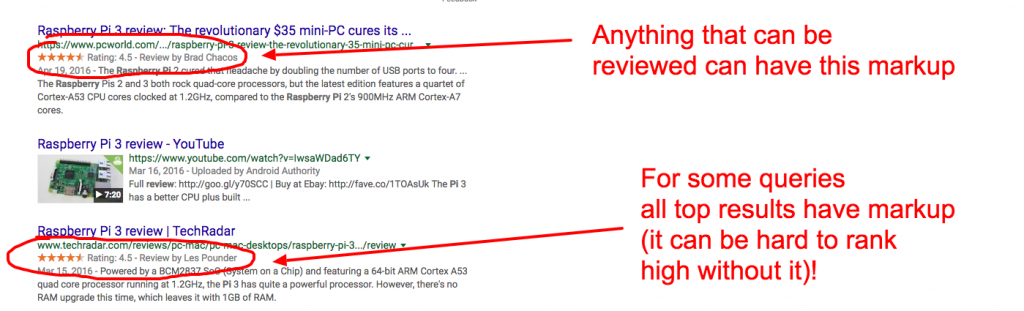
Structured Data Markup
Structured Data Markup is code that adds context to your content. It describes the data on your website specifically so that a search engine may understand it. This helps push your page on top of the search results if the user’s search context matches what you’ve specified on the website. An example of this is a recipe tag that shows your page in the search results for recipes if the user searches for a specific one that you happen to have on your website.
Check Canonical URLs:
A canonical URL is a simple way of telling Google which version of a page to index. This helps avoid duplicate content issues. It can be set using rel=”canonical” link tag in the site’s HTML pages.
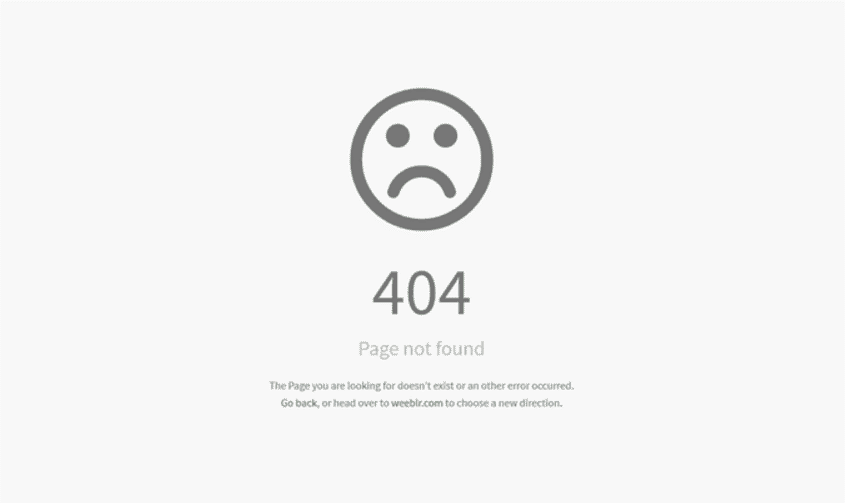
404-page Optimization
A 404 page is when the user mistypes or tries to go to a page on the website that doesn’t exist. In that case, a 404 page neatly handles the exception and redirects the user to the helpful content. A structured 404-page will prevent confusion for the search engine when it crawls and hits an unknown page.
Optimize XML Sitemap
The XML sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website. It also includes information like publication date and updated date. This is handled in most CMSs but if you are running a custom website, this is something to keep in mind. This one has to be kept clean and uncluttered with useless information like dead pages or author pages.
Get an SSL Certificate
HTTPS protocol lets the user know that the site is secure. Google drastically prefers secure sites to non-ssl sites. Google has started showing warnings in Chrome when the site is not HTTPS. Users might be wary of visiting your site if a warning pops up in the browser. This is a small problem with an easy fix.
Website Loading Speed
The website should be fast to load. If it takes a lot of time to show up then Google will not prioritize it in the search results. You should check whether your site needs optimization using Google Page Speed Insights, pingdom tools, and google mobile speed tool. This is more of an engineering problem. Here are steps that you can take for this subcategory:
- Upgrade the server to 64 bit OS.
- Upgrade to the latest version of PHP.
- Reduce image sizes.
- Minimize plugin use as it slows down download speeds.
- If you are using WordPress always keep it updated to the latest version along with all the plugins.
- Don’t use very general pre-made themes.
- Optimize and minify CSS and JS files.
- Use a caching plugin to serve cached pages.
- Keep the head tag of your website light.
- Use AJAX wherever possible.
- Use a CDN for popular libraries and static files.
- Speed test your web host. Look at user reviews to find a provider that offers good speeds.
- TTFB(Time to First Byte) which is a metric about the time needed for a browser to load the first byte of your web page’s data should be minimized.
- Reduce CSS image requests.
- All content that is served should have HTTP compression.
Mobile Responsive Website
A website has to be mobile-friendly or else it gets low preference in Google’s SERPs. Most people are using the internet and Googling on their phones. Hence this metric is very important for Google. Use of frameworks such as Bootstrap will ensure that your site is responsive and auto resizes on all sizes of screens. The website should also be small enough to load on 3G speeds in less than 6-7 seconds. Popups should be strictly avoided on mobile sites.
Consider AMP Support
Accelerated Mobile Pages in Google’s initiative to make the mobile web faster. It loads the website through Google’s caching servers and hence is much faster. It is only shown to Google Mobile results, but it will really improve your search results ranking. This is hard to implement, and you’ll have to hire a developer to build a site with AMP. There is a chance to potentially increase your CTR from mobile users.
Pagination
Pagination is when you want to divide a long page into multiple smaller pages. To consolidate the links you can use rel=”next” and rel=”prev” link tags to tell the search engine that the subsequent pages are a continuation of the first page.
Multi-Lingual Websites
You can use the hreflang attribute to give Google more info about the site structure and content. This way users from a particular country will get served the right content in their own language.
All of the aforementioned technical aspects can benefit your SEO efforts if executed properly. Whether you capitalize on one, some, or all of these opportunities, your site will be better off during search engine crawls because of it.
Authorship: Taj R.